________________________________________________________________
What Does That Word Mean?
This glossary is a list of words that are often used with computers in schools. Some words are common computer words, some are special words used to describe things in the A+LS program. The list is in alphabetical order and you can jump ahead in the list by clicking on one of the links below.
When reading the meaning of a word, watch for special colored and underlined words. They are also defined in this glossary. For example, in the definition of account below, the words rights, administrator, username, and password are all colored and underlined. That indicates that those words are also explained in this glossary.
A
account - To limit access and increase security on networks, anyone wanting to use the network has to have an account setup for them by the network administrator. The account gives a user rights to some of the network's shareable resources. To access an account a user typically has to enter their username and password. [Previous page]
administrator - The person in charge of a network or server is called the administrator. When you attempt to use a network resource and are unable to, you should contact the administrator. Also see rights. [Previous page]
alignment - Usually text (numbers or letters) that can be horizontally aligned with the left or right side of the workspace. Text can also be center aligned. Full justification aligns the text to both the right and left side simultaneously by stretching the spaces between words. Vertical alignment of objects is also available in graphic, presentation, and desktop publishing programs. [Previous page]
A+LS - A+nyWhere Learning System; the K-12 curriculum system from The American Education
Corporation. [Previous page]
application - A software program used for a particular kind of work, such as a spreadsheet or word processor. Microsoft Word is an application. [Previous page]
argument - A string, value, location, or condition that you provide for a function. When searching on the Web, many search engines accept Boolean arguments (also known as queries) that use common English words such as AND and NOT. For example, a search argument might be: car AND Germany NOT Mercedes. That would bring up information about German cars such as VW and BMW but not Mercedes. Also see SQL. [Previous page]
B
bit - Abbreviation for binary digit. A binary digit may have one of two values - 1 (on) or 0 (off). Bits, on and off, are a computer's native language. All digital information is stored in 1s and 0s. Typically 8 bits make up one byte. [Previous page]
bookmarking - In the A+LS system, if a teacher has turned on bookmarking, students can exit a partially completed test and return later to finish it. But students should answer all of the questions they’ve seen so far, because they won't be able to change their answers when they return.
In Progress incomplete tests will have a Score of "0/0" listed for each time the student entered the test. Only complete, graded test sessions will show a Maximum Score greater than "0" (the number to the right of the "/"). [Previous page]
broadband - Usually refers to a high speed connection to a remote location or the Internet. For many computer users, broadband means having a cable modem or DSL connection to the Web. [Previous page]
browser - A browser is the program on a computer used to surf or browse the Web. Common browsers are Microsoft® Internet ExplorerTM and Google® Chrome. [Previous page]
button - Works like a button on a TV or other appliance, clicking on it sends a command to the computer. Buttons may have words on them or icons (pictures) that indicate what the command does. For example, a graphic picture (icon) of a stop sign, placed on a button, is used to represent the command to quit a lesson in the A+LS system (note the Stop button on the button bar pictured below). [Previous page]
button bar - Also known as a toolbar; it consists of a row of small buttons, each with an icon (picture) that represents a command; usually found beneath the title bar or menu bar near the top of the program's window. When you click on one of the buttons, a command is executed, a dialog box opens, or a menu displays. [Previous page]
Button Bar or Toolbar (circled in red)
byte - The basic unit of computer memory, large enough to hold one character of alphanumeric data. A byte consists of eight bits. A kilobyte (a "K" or "KB") is a thousand bytes, while a megabyte (or "MB") is a million bytes. Really big amounts of bytes are gigabyte (a billion bytes) and terabyte (a trillion bytes). [Previous page]
C
cache - Using RAM (memory) to optimize data transfers between system components with different performance characteristics, for example from a disk to main memory. Sometimes the hard drive is used to cache information from the Internet. Whatever the components involved, the one used as the cache is always much faster than the source, resulting in a performance advantage. [Previous page]
CD-ROM - Compact Disc-Read Only Memory; a storage medium for programs and information. Discs store information in ways that prevent change or erasure. A CD-ROM holds between 650 and 700 megabytes of information. [Previous page]
cell - A spreadsheet is made up of little boxes called cells, the unit of the worksheet that stores data. Cells are located by column and row coordinates. For example, A1 is the upper left-most cell in a spreadsheet. The cell A2 is immediately below it and B1 is to the right of A1. Numbers, text, and formulas can be entered into a cell. [Previous page]
checkbox - Many programs will let you customize them. One of the methods used to select a program
option is the checkbox. It's quite intuitive:
 = unchecked = not selected, option not enabled = unchecked = not selected, option not enabled
 = checked = selected, option enabled
= checked = selected, option enabled
You click in the checkbox to toggle the checkmarks on and off.
[Previous page]
choose - Using a mouse or key combination to pick an item that begins an action. [Previous page]
click - To quickly press and release the mouse button, typically using the left button. On a tablet, tapping on an object is used instead of clicking. [Previous page]
client - Computers or programs that require a network server to function. One example is your e-mail client. Your email software is probably loaded on your hard drive, but it is useless without access to the server that receives the e-mail. [Previous page]
clipboard - A temporary storage location in computer memory that enables you to copy or move
information from one place on screen to another place or across applications. Common Windows
menu bar commands are Edit/Copy which copies the selected information (often text) to the
clipboard, then Edit/Paste takes it from the clipboard and places it where the cursor is located. [Previous page]
close window button - On computers using Microsoft Windows, this button is used to quickly close a window or a program. You click on the close button, located in the upper right corner of most windows and the window will disappear. [Previous page]
Close Window Button (circled in red)
column - A vertical list of information representing a single type of information, such as an assignment or score. A+LS Progress Records (see the figure below) are made up of several columns, each with a column header at the top that describes the information in the column. A column can be a vertical block of cells that runs the entire length of a worksheet. There are 256 columns in an Excel worksheet. [Previous page]
 Column (circled in red)
Column (circled in red)
column headers - The label at the top of a column, indicating the type of information in the column. Sometimes these are also command buttons that will sort the list of information in order based on the selected column header. For example, when looking at a list of files in Windows Explorer, you can sort them by date by clicking on the Modified column header. To sort it alphabetically (A-Z) by filename click on the first column header, Name. Clicking again will sort it in reverse order (Z-A). [Previous page]
command - An instruction you give to a program. To select a command, click the mouse in a menu or
use the appropriate hot key. [Previous page]
command keys - Combinations of [Alt] or [Ctrl] and a letter or number key that execute commonly used commands. Command keys, also known as "hot keys", reduce the number of keystrokes for performing a number of tasks. [Previous page]
configuration - The settings that control how a program or Windows is setup. May also refer to the computer's hardware. An example of a software/hardware configuration; you probably have a printer connected to your computer and Windows is configured to understand that printer's specific commands. An example of a hardware configuration is the amount of RAM (memory) your computer has. [Previous page]
CPU - Acronym for Central Processing Unit. The microprocessor chip that performs the bulk of data processing in a computer. Intel's Pentium line of CPUs is the one most commonly found in computers today. [Previous page]
cursor keys - The four keys on the keyboard with directional arrows, typically located between the numeric keypad on the right and the letter keys on the left. When in a text document, pressing the down cursor key will move the text cursor on screen, down one line. [Previous page]
cursors - There are two basic types of cursors, mouse and text. The mouse cursor moves about the screen when you move the mouse and is usually represented by a white arrow (see graphic below). You point with it and click to issue commands to the computer. The text cursor is usually a black vertical bar which indicates where text will appear when you type. You can move the text cursor by clicking with the mouse cursor. [Previous page]
Mouse Cursor (circled in red)
D
database - An organized collection of related information, like an office filing cabinet. Some A+LS databases have many thousands of records, each containing one kind of information (class, user,
lesson, etc.). A group of fields make up one record, and a number of records make up the database. [Previous page]
default setting - The setting a program uses automatically unless you specify another setting. If you see a button that says something like "Set Default," it will restore the default settings, overwriting your custom settings. [Previous page]
desktop - The screen background for Windows that enables you to perform tasks electronically, as you
would do manually at your own desk. The desktop is similar to the work surface of a desk you might use at work, school, or home. [Previous page]
dialog box - A specialized window that opens to ask you for input. Often the choices are expressed as buttons; OK, Cancel, Finish or Help. Some dialog boxes, for example Save As (see the graphic below), request you to input text. [Previous page]
Save As Dialog Box
dial-up - How a network user connects to a network via a phone modem. [Previous page]
directory - A subdivision of a disk. You can create and name a directory and store related files in it when you save the files to disk. You can also create subdirectories within directories. Directories are also called folders in some books and manuals. [Previous page]
disc - A storage medium for programs and information. Discs store information in ways that use optically written data. Examples of discs are CD-ROMs, CD-RWs (CD-Read/Write), and DVD-ROMs. Hint: disc with a "c" is an optical media. [Previous page]
disk - A storage medium for your work. Disks store information magnetically and are usually floppy disks or hard disks. Data on disks can be written to, read, and deleted. Hint: disk with a "k" means magnetic storage (like hard drives), but disc with a "c" means it is optical (like a CDs). [Previous page]
disk/disc drive - The device that holds a disk while the computer reads and writes data to it. Hard drives hold disks that can't be removed. Other disk drives, such as CD-ROM drives, let you remove the media. [Previous page]
double click - Clicking the mouse button twice in rapid succession without moving the mouse. Double-clicking on an icon often loads a program. [Previous page]
drive letter - The letter followed by a colon that identifies which disk drive is to be used. Typical Windows computer systems use:
A: and B: - Floppy disk drives
C: - Local hard drive
D: and/or E: - Local CD-ROM drive or a second hard drive
F: thru Z: - Network drive letters
[Previous page]
driver - When a computer needs to interact with a new piece of hardware or software it may need a special piece of programming called a driver. The driver acts as a go-between or translator between the new item and the computer. [Previous page]
drop box - Also known as a combo box, it is a common method for changing program settings. They display as text next to a downward pointing arrow. Click on the downward arrow and more choices drop down (hence the name drop box). Then click on your preference to change the setting. Note the graphic below, the arrow shows how the box drops open when clicked. [Previous page]

Drop Box or Combo Box
E
error message - A message that appears, usually in a dialog box, when a program detects a mistake or cannot perform a task. Often you can select Help to get more information or click OK to clear the error. [Previous page]
extension - A . (period) followed by a suffix of up to three characters at the end of a filename. Examples: .TXT is a text file, .PDF is a Portable Document File for Adobe Acrobat, and .DOC is an MS Word document file. Many applications automatically assign extensions to their files. It is strongly advised that you DO NOT change a file extension or the application that created it may have problems opening it later. [Previous page]
F
field - A labeled column in a database that contains the same kind of information for each record. For example, the FIRSTNAME field will contain all the first names in a database. [Previous page]
file - A collection of information stored under a single name on a disk. A file can be a program, part of a program, or a data file, such as a word processing document. [Previous page]
filename - The name you give to a file on a disk. In Windows, filenames can be up to 64 characters in length. Also see extension. [Previous page]
folder - A subdivision of a disk. You can create and name a folder and store related files in it when you save the files to disk. You can also create subfolders within folders. Folders are also called
directories in some books and manuals. [Previous page]
font - A typeface of a particular visual style that a program uses for text when printing. A font size is usually measured in points: 72 points equals one inch. Windows comes with three basic fonts, Arial, Courier, and Times Roman (the font used for this glossary). [Previous page]
format - You can format information to display in a particular way. For example, you can take a section of text and reformat the font so the words are unique looking, the letters are bigger and more colorful. Formatting can also mean preparing a disk to receive data. [Previous page]
function keys - Keys [F1] through [F12] on your keyboard, which perform special functions in some programs. [F1] is the Help key in many programs, including Microsoft OfficeTM. [Previous page]
G
GB - Short for gigabyte (a billion bytes). As the capacity of computers has grown over the years, more parts are being measured in the billions. The most common computer part measured in GBs is a hard drive. [Previous page]
group - A collection of applications. For example, if you click on the Windows Start button, you'll see the Programs group, which, when highlighted, reveals other groups of applications under it. Inside an application's group are icons that, when double-clicked, load the applications. [Previous page]
H
hard disk - See hard drive.
hard drive - A permanent storage device that has a much greater capacity than a floppy disk or CD-ROM. A hard drive uses several metal or glass platters, spinning at thousands of RPMs, to store computer programs and data magnetically. [Previous page]
highlight - To select (mark) an object or text item. Highlighted information usually appears in reverse video, i.e. a highlighted file in a file list will have a black or dark blue box over it, with text
appearing in white. [Previous page]
hot key - Sometimes known as a shortcut key; a hot key is a combination of keystrokes (usually two) that are short for a frequently used command. For example, [Ctrl] P is a common Windows hot key that brings up the printer dialog box, saving several clicks. [Previous page]
I
icon - A picture used to represent commands, programs, and other items. For example, a graphic picture of a stop sign, an icon, is used as a button to represent the command to quit a lesson in the A+LS Client (Webstart). Icons are also found on the Windows desktop. They often symbolize links to programs, so when you double click on or tap an icon, that program will load. [Previous page]

An Icon Used As a Button.
J
Java - A computer programming language frequently used for writing networked programs. The A+LS Remote Client was written using Java. [Previous page]
K
K or KB - Short for kilobyte (a thousand bytes). It used to be that many things on a computer were measured in Ks, but computer sizes have grown so much that MBs (megabytes) are much more common. Now only small text and graphic files are still measured in Ks. [Previous page]
L
label - Descriptive text used to identify data. Often a label is found at the top of a column, describing the type of data that is displayed in the column. See graphic below. [Previous page]
 Label (circled in red)
Label (circled in red)
LAN - Local Area Networks (LANs) are a common method for connecting numerous workstations to shared resources such as servers and printers. Typically LANs are, as their name indicates, local resources, usually limited to a single building or campus. Also see WAN (Wide Area Network). [Previous page]
log on - The process of connecting to a network or networked software. To log on usually consists of typing in your log-on name and password. After the network server has validated your log-on name and password, it gives you access to the resources you have rights to use. [Previous page]
log-on name - Each person using a shared or networked piece of software is given a log-on name. Each log-on name is unique, so you are the only person using that software with that log-on name. Usually, when you first load the software you are asked to type in your log-on name and after that, your password. Typing them both in is called logging on. After you have logged on, you are able to use the software. [Previous page]
M
maximize window button - On computers using Microsoft Windows, this button is used to enlarge the active window to fill the entire desktop. When the window is maximized, this button toggles (on/off) into the Restore button which returns the window to its previous size. [Previous page]
Maximize Window Button (circled in red)
MB - Short for megabyte (a million bytes). Several parts in a computer are measured in MBs, for example RAM (128MB) and floppy disks (1.44MB). [Previous page]
memory - See RAM.
menu - A list of items. Most menu items are commands or functions that the program carries out when an item is selected. [Previous page]
menu bar - Row of menu commands (text) which usually starts in the upper-left corner of the program's window. When you click on one of the words, a list of choices displays, dropping down from the menu bar. Often the first commands are File and Edit. [Previous page]
Menu Bar (circled in red)
minimize window button - On computers using Microsoft Windows, this button is used to shrink the active window down to the taskbar (Windows 95/98/NT/ME/2000). Please note that this does NOT close the program, it is still running in the background, and can be restored to the screen by clicking on its button on the taskbar. [Previous page]
Minimize Window Button (circled in red)
modem - Modem is becoming a generic term for a device that connects a home computer to the Internet.
Contemporary examples are cable modems, DSL modems, and classic telephone modems.
Originally modem was all capitalized, MODEM and meant MODulate-DEModulate, the process of
converting a telephone signal into a computer signal. [Previous page]
module - A module can be either a related program or a preprogrammed data set. Examples of a related program would be the word processor module in Microsoft Works or the essay module in the
A+LS system. An example of a packaged data set is one of the A+LS system's curriculum modules, like Mathematics III (grade three math). [Previous page]
N
network - A system in which computers are connected to each other so they can share information and
resources. Computer networks are changing the way people communicate, distribute, and share
information. There are many different ways information can be accessed, shared, or communicated via a network. Computer networks are being used to access software applications (like Microsoft Office) running on a file server, send e-mail to someone in England or Japan, and distribute the company's newsletter to people around the world.
Networks can be classified according to their geographical size; Local Area Network (LAN) and Wide Area Network (WAN). They can also be grouped by their function; internal company network (Intranet) vs. external network (Internet) or other factors. [Previous page]
O
ODBC database - Abbreviation of Open DataBase Connectivity, a standard database access method developed by Microsoft Corporation. The goal of ODBC is to make it possible to access any data from any application, regardless of which database management system (DBMS) is handling the data. ODBC manages this by inserting a middle layer, called a database driver, between an application, and the DBMS. The purpose of this layer is to translate the application's data queries into commands that the DBMS understands. For this to work, both the application and the DBMS must be ODBC-compliant--that is, the application must be capable of issuing ODBC commands and the DBMS must be capable of responding to them. The ODBC standard supports SQL. [Previous page]
P
password - The first line of defense for any network are user passwords. Each user is assigned a unique name and a secret password. Keeping the password a secret limits access to the network to just authorized users. Hint: toss a number into your password to make it harder for other folks to guess. For example dog2cat, birdbrain6 or 8hamburger, something easy to remember but hard to guess is the goal. Never write down a password, it is like your bank PIN number. [Previous page]
path - A name used to identify the location of files or folders (directories) on a disk. For example the path for the A+LS Remote Client on a Windows computer is:
C:\als30\alsclient
The C: represents the drive letter, in this case your local hard drive. The \ is a separator, indicating that what follows is a new item. In this case, there are three folders nested inside one another like one of those Russian wooden dolls that's a doll, inside a doll, inside a doll. [Previous page]
peripheral - A device added to a system as a complement to the basic CPU, such as a disk drive, scanner, tape drive or printer. [Previous page]
point - To slide the mouse until the mouse's cursor or pointer rests on the item of your choice. Also a unit for measuring font size, see font. [Previous page]
pop-up menu - Right clicking on an object will sometimes open a pop-up menu. This little menu only shows you commands that apply to the object on which you right clicked. Some programs make extensive use of pop-ups. See figure below. [Previous page]
Internet Explorer Pop-up Menu on All White Page
Q
query - Asking a database for information using a specialized language. For example, the query:
SELECT ALL WHERE age > 30 AND name = "Smith"
requests all records in which the name-field is "Smith" and the Age field has a value greater than 30. The de facto standard for query languages is SQL. [Previous page]
R
RAM (Random Access Memory) - The temporary storage area, also called conventional or main memory, in which your computer runs programs and holds their data while you work on them. You have to save your work because the data in RAM disappears when the program is closed or the computer's power is turned off. [Previous page]
record - A set of database information, often displayed on screen as one horizontal row. The A+LS Progress Report (see figure below) displays part of an activity record on each row, with Assignment, Score, and Type information. The A+LS system is made up of many thousands of records, some containing lesson data, others class or user information. [Previous page]
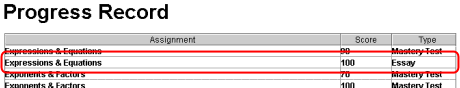 Record (circled in red)
Record (circled in red)
restore window button - On computers using Microsoft Windows, this button is used to reduce a maximized window to its previous size. When the window is less than the full desktop, this button toggles (on/off) into the Maximize button which expands the desktop to its full size. [Previous page]
Restore Window Button (circled in red)
retrieve - To load a data file from the hard disk, network or floppy disk into RAM, making it the current lesson, sound, or graphic. The A+LS Remote Client can retrieve lesson data from a database located across the country via the Internet. [Previous page]
rights - Network security revolves around rights or who can use what shared resources. Rights can include the right to view or modify files or other network objects. Some network-based programs, such as the A+LS system, are also rights-based. Rights can focus on specific resources, like the right to edit lesson files for yourself or globally (editing lesson files for the whole school). [Previous page]
root directory - If you think of a computer's file structure as a tree, with the branches being folders and the leaves individual files, then the root directory is at the very base of the tree (hence "root"). The root drive for almost all Windows computers is C: (the root drive is a single letter C, followed by a colon). [Previous page]
row - A horizontal block of cells that runs across the entire width of a report or worksheet. In a database, a row typically represents a database record. In the A+LS Progress Report below, the row is the record of a student's progress on a single assignment. [Previous page]
 Row (circled in red)
Row (circled in red)
S
save - To take a copy of the data in the computer memory (RAM) and store it in a file on a disk. Saving is useful because data in memory disappears when the computer is turned off.[Previous page]
scroll bar - Used to move up, down, left, or right in a document or window. Every scroll bar has a pair of scroll buttons and a scroll box that moves along the scroll bar. See the graphic below. Click here for a brief tutorial. [Previous page]
scroll box - The button that floats along a scroll bar indicating your relative position in a window (shown in the graphic above). By dragging the scroll box along the scroll bar you slide the view horizontally or vertically on the screen. This is a good way to browse a document or Web screen. Click here for a brief tutorial. [Previous page]
scroll buttons - The arrow buttons on a scroll bar used to change what is displayed in a window a little bit at a time. A screen can often be scrolled up or down as well as right or left. The top and bottom scroll buttons are shown in the graphic above. Click here for a brief tutorial. [Previous page]
scrolling - Using the scroll bar or cursor keys to change the view of the current program on the screen. Click here for a brief tutorial. [Previous page]
select - To mark an item by by clicking it with a mouse or highlighting it with key combinations. [Previous page]
server - A computer that provides networked workstations with controlled access to shareable resources. The resources can be printers, file storage space, applications, and even scanners or copy machines. To maintain the integrity of the server and the files and programs located on it, security is always a concern. A username and password are almost always required to use shared resources. [Previous page]
shortcut - A link you can place in any location that gives you instant access to a particular file, folder or program. It can link to objects on your local hard drive or network. It is important to understand that deleting a shortcut has no effect on the target object linked to it. For example, you have a shortcut on your desktop to load Notepad. If you delete the shortcut, Notepad will still work. You just have to load it through its program group icon. [Previous page]
sort - To arrange the records in a database into a particular order. It is common to sort objects into alphabetical order (A to Z). You can also sort by a field such as state or zipcode. [Previous page]
spreadsheet - A program that can be used like a financial ledger sheet. Made up of rows and columns, the spreadsheet primarily works with numbers, adding, subtracting, and much more. It was the "killer app"; (application) that first popularized microcomputers in the late 1970s. [Previous page]
SQL - Abbreviation of Structured Query Language, and pronounced either "see-kwell" or as separate letters. SQL is a standardized query language for requesting information from a database. [Previous page]
stateless sessions - The Internet can be a very effective tool for education, but it is never 100% reliable. No matter how good your connection is or should be, things can and do go wrong.
Because you can experience connectivity problems outside of the control of the American Education Corporation, we implemented a feature called stateless sessions. This allows the software to save a student's place in a lesson if the connection is lost for whatever reason. So student work is not lost just because the connection is. When the connection is re-established and the student logs on again, the program retrieves that session from the database so it can be resumed and the lesson completed.
The message that displays at logon, "Resuming your previous A+LS session" lets the student know he or she will be returning to the previously saved session and the last assignment worked on.
These stateless sessions are saved when the student abruptly loses connection to the server. They are also saved if the student shuts down the browser without exiting the software properly. Students should never close their browser when exiting a lesson until after they've seen the "Exiting Curriculum Module" screen. If they shutdown the browser too soon, it will save a session for them and later return them to the lesson they thought they had exited. This will also happen if they try to refresh the browser ([F5] in Windows systems). [Previous page]
subdirectory - A subdivision of a directory on a disk. Also known as a folder. [Previous page]
T
taskbar - The gray bar that appears at the bottom of the Windows desktop. The taskbar contains the Start button, minimized programs, and the System Tray (programs running in the background such as anti-virus programs and audio volume controls). [Previous page]
title bar - Displays the name (or title) of an application, module, or document. When on screen, it is the very top bar at the top of a program window. [Previous page]
Title Bar (circled in red)
toolbars - Often made up of a group of buttons, small icons (pictures), and/or text commands. Toolbars provide quick access to frequently used commands and procedures. [Previous page]

A+LS Client (Webstart) Toolbar (circled in red)
Sometimes toolbars don't have obvious buttons, instead they have words or icons to click on. The A+LS toolbar used in Browser Playback mode is a good example of one that has icons you can select (see the graphic below). [Previous page]

A+LS Browser Client Toolbar with Selectable Icons
U
user - A user is a person who has been granted use of one or more shared resources on a program or network. Users are typically assigned log-on information (username and password). Also see username below. [Previous page]
username - To log on to a network requires a unique username. This ensures that the network grants you only those rights that you are entitled to. [Previous page]
V
W
WAN - Wide Area Networks, WANs, are typically defined as a collection of servers and workstations that are interconnected yet located in multiple geographic locations. Rather than define specific
technologies, WANs are a description of the size and scope of a network. [Previous page]
window - A rectangular area that displays a software application or a document file. Windows can be
opened, closed, resized, and moved. You can have several windows open on the desktop at the
same time. Also see close, maximize, and restore window buttons. [Previous page]
X Y Z
________________________________________________________________
|